In recent years, more and more businesses have moved to the cloud. And why not? Cloud computing offers greater flexibility, productivity, scalability, and data redundancy at a fraction of the cost of on-premise solutions. You are also likely to find yourself paying less for state-of-the-art security than you would if you had stayed on-premise. That said, it certainly comes with its own set of challenges.
A cloud computing study conducted in 2022 reported that 42% of enterprises struggle with data privacy and security issues the most. But despite these struggles, 92% of organizations use some form of cloud infrastructure to host their data.
With the exponentially growing popularity of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS platforms, Cloud will remain the dominant form of data storage. This is why it’s crucial to be aware of the security challenges you might encounter when you use Cloud services.
Data breaches

The frequency of data breaches associated with cloud-based services has increased over the years. According to the 2021 Thales Global Cloud Security Study, 40% of organizations have experienced a cloud-based data breach. Even Microsoft, one of the biggest tech companies in the world, is not impervious to this problem. In 2021, 38 million Microsoft customer records were exposed due to misconfigured Microsoft Power Apps portal settings, and again in 2022, a hacker group called Lapsus$ breached Microsoft Azure DevOps.
This goes to show that data breaches can occur in a number of ways, like a cyberattack, an insider leak, a misconfiguration, or an unintentional disclosure. If you fail to deal with your data breaches properly, you could open the floodgates for penalties, fines, and compliance risks. Not to mention the erosion of customer trust in your company.
Insider threats
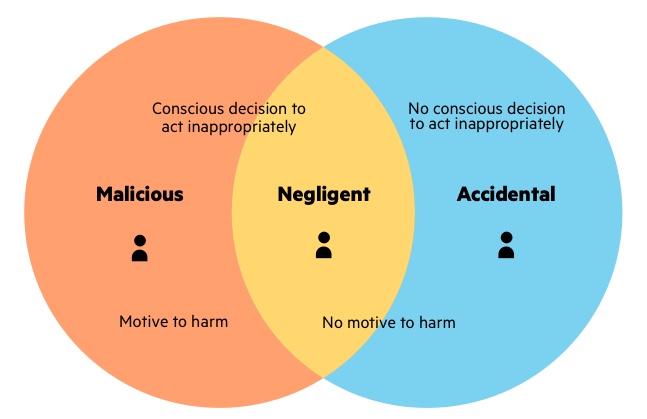
Employees can be a cybersecurity risk, whether they mean to or not. In fact, according to Intel, 40% of all data breaches are caused by internal actors—with half of them being intentional and the other half being accidental.
You will be surprised at how easily an outside attacker can get into your system by cracking your employees’ weak passwords. Fortunately, this problem can be easily rectified by automatically scanning for weak passwords and making 12-character passwords with numbers, symbols, and upper and lowercase letters mandatory. You should also make it a habit to regularly ask employees to update their passwords.
Other insider threats to your organization include malicious employees, departing employees, third-party partners, and more. Such threats can result in corporate espionage, fraud, intellectual property theft, and more.
DDOS (or Distributed Denial of Service) attacks
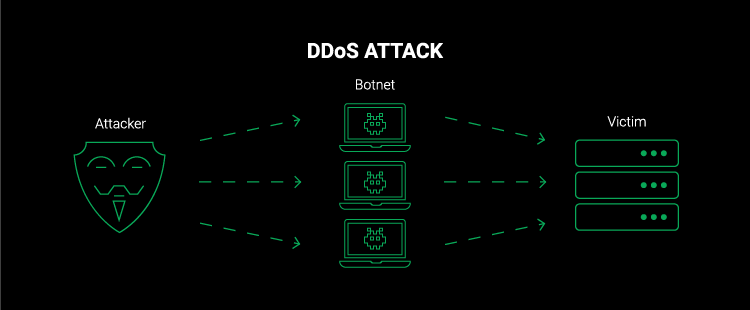
The acronym DDOS stands for “distributed denial of service,” a type of attack in which multiple computer systems attack a target server by sending large data overhead packets. The goal of DDOS attacks is to overwhelm the server to the point where it can’t respond to legitimate user requests.
In 2022, Amazon Web Services experienced the largest reported DDOS attack when it was hit with a peak traffic volume of 2.3 terabytes per second. Thankfully, it was mitigated by AWS Shield, which is designed to protect against DDOS attacks.
That’s why DDOS protection is necessary for any cloud service, website, or web-based application. Without it, downtimes can last for hours or even days and damage your brand’s reputation and disrupt revenue.
Unauthorized user access control
The biggest advantage of cloud services is that you can access your data from anywhere, at any time. However, this also makes it more difficult to control who has access to your data. With on-premises software, your data run on a local network—but with cloud services, your data is accessed through the internet, making it easier for anyone (including hackers) to gain unauthorized access.
One of the most popular ways to gain access illegally is through stolen credentials. This is why it’s crucial for organizations to implement multi-level or multi-factor authentication for entry. With an MLA, two or more identification criteria are used before giving access. You can use anything from one-time passwords (OTPs) and personal identification numbers (PINs) to biometrics and keycards, to set up an MLA.
At the end of the day, you must control who accesses your data or how they access it. Otherwise, you create vulnerabilities in the system that can be exploited by hackers.
Insecure APIs
APIs or Application Programming Interfaces are a set of protocols that allows two or more software applications to talk to each other. Cloud services provide different apps and interfaces that make it easier for customers to access data or perform certain tasks.
These APIs, however, are a cloud service’s most exposed component and therefore the most likely to be hacked if not secured properly. As such, both cloud service providers and their customers have a duty to secure these APIs.
To ensure the security of your API endpoints, you can use a web application firewall, API protection (WAAP), authentication tokens, API keys, reCAPTCHA, TLS (Transport layer security) and always connect over HTTP. These are some of the methods by which both cloud service providers and customers can ensure the safety of their API endpoints.
Suggested Read: Why Big Data Analytics is The Best Decision for a Career
Conclusion
Cloud security is a tough nut to crack, but that’s no excuse for leaving your data unprotected. The good news is that if you’re vigilant, you can mitigate these challenges and become safer against all kinds of security threats. With the right cloud services provider and taking cybersecurity measures on your end, you can better protect your organization from the dangers of cybercrime.
Shivani Sehta is a marketing enthusiast and content writer at World Fashion Exchange, a leading Fashion ERP Software and PLM software company. She specializes in writing content about the latest technology trends. In her free time, she likes to dance and spend time with nature.